Copyright Priory Lodge Education Ltd. 2005
First Published 17th June 2005
Case report : pineal metastasis from lung cancer
Dr. K.W. Lam1 MRCS , Dr F C Cheung 2FRCS , FHKAM , Dr K M Ko 1 FRCS , FHKAM
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery1 ,Department of Neurosurgery 2, Queen
Elizabeth Hospital, 30 Gascoigne Road, Hong Kong.
Correspondence :
Dr K.W. Lam , fax : 00852- 2958-5673 , email : pkwlam1@yahoo.com
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital , 30 Gascoigne
Road, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Running title
Metastasis to the pineal gland from carcinoma of lung are rare.2 This is a
case report of a 57 year old lady presented with progressive diplopia,
nausea and headache. CT brain revealed pineal metastasis from lung
cancer with evidence of hydrocephalus. PET scan reviewed primary lung
tumor in the right hilar region and presence of diffuse metastasis in
multiple lymph node and bone. 5 year survival in patients with lung cancer
stage M1 disease, according to International System for Staging Lung
Cancer 7, was expected to be around 1%. Glucorticoid and external whole
brain radiotherapy increased the median survival from one month up to six
months.10
Abstract
Metastasis to the pineal gland from carcinoma of lung are rare.2
This is a case report of a 57 year old lady with multinodular goiter,
presented with 2 months' history of progressive diplopia, nausea and
headache. CT brain revealed pineal metastasis from lung cancer with
evidence of hydrocephalus. Emergency CSF diversion surgery
(ventriculoperitoneal shunt, VPS) had been carried out to relieve the
hydrocephalus. Debulking of the tumor by stereotactic surgery (X-knife)
was, subsequently performed. Metastastic adenocarcinoma was confirmed
histologically by endoscopic ultrasound guided aspiration of her
supra-clavicular lymph node. PET scan reviewed primary lung tumor in the
right hilar region and the presence of diffuse metastasis in multiple lymph
node and bone. She received external whole brain radiotherapy , WRBT
(53.4 Gy) and was followed up in out-patient clinic.
5 year survival in patients with lung cancer stage M1 disease, according to
International System for Staging Lung Cancer 7, was expected to be around
1%. Glucorticoid and external whole brain radiotherapy increased the
median survival from one month up to six months.10
Keywords : lung cancer, pineal metastasis, staging, survival
Introduction
Pineal region tumors make up 0.4-1.0% of intracranial tumors in
adults.3Central nervous system metastases occur in less than 3% of
all asymptomatic lung cancer patients. 2 Metastasis from carcinoma
of lung to the pineal gland are rare.2
When present, the features of diplopia associated with headache,
nausea and vomiting and papilloedema (on fundal examination), one
should point to the diagnosis of increase intracranial pressure. Brain
masses (eg tumor, metastasis) should be part of the differential
diagnosis. If left untreated, aqueductal compression with
hydrocephalus may progressed to lethargy, obtundation, and death.4
There had been relatively few reports on this type of metastasis
offering discussion of diagnosis and treatment modalities. 4
Case report
A 57 year old lady has history of multinodular goiter, presented with
2 months history of dizziness, headache and vomiting. A month later,
she complained of progressive worsening of diplopia.
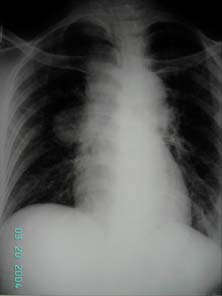
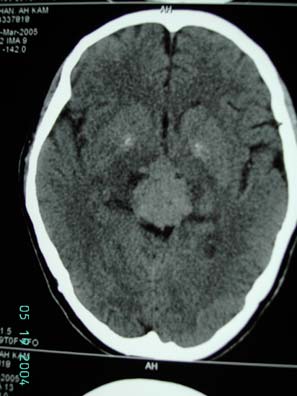
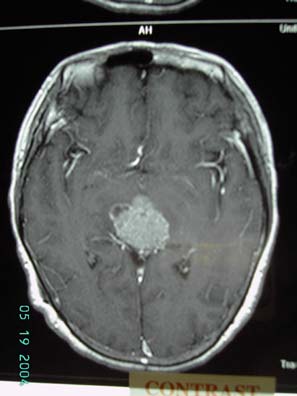
figure 1
figure 2
Figure 1 CXR showing right hilar
Figure 2 CT scan showed 32x28x26 mm hyperdense
ma
ss
homogenous contrast enhancing solid mass over midline above
mi
dlin
e causi
ng obstructive hydrocephalus
Figure 3 MRI scan showing mass in pineal
region enhanced in T2 images with mass
effect
figure 3
On examination, pupil size were unequal, 3mm (right) and 2mm
(left) and fundal examination revealed bilateral papilloedema.
Multiple cervical lymph nodes were palpable on the right side.
Neurological examination were otherwise unremarkable. Glascow
coma scale was 15/15. Tumor markers including serum human
chorionic gondaotrophin (ßHCG), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP),
carcino-embrogenic antigen (CEA) were within normal ranges. Chest
XR showed right hilar mass.(figure 1) CT scan of brain showed a 32 x
28 x 26 mm hyperdense homogenous contrast enhancing solid mass
crossing over the midline causing obstructive hydrocephalus. There
was no evidence of tumor invasion into third ventricle or cerebellar
vermis. (figure 2)
Emergency ventriculo-peritoneal (VP) shunting for CSF diversion
and relief of hydrocephalus was carried out.
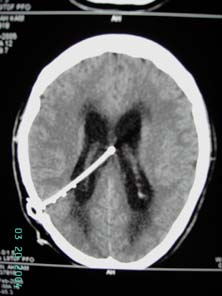
Figure 4
post-op CT brain showing decompression
of ventricules with ventriculo-peritoneal
shunt in situ
figure 4
Endoscopic ultrasound guided aspiration to supraclavicular lymph
node confirmed metastatic adenocarcinoma, spread from her
primary lung cancer. Her visual symptoms persisted post-operatively.
Stereotactic surgery (X-knife) was performed for debulking of the
tumor mass.
18-FDG Whole body PET scan showed increase FDG uptake in
multiple areas including the pineal area (SUVmax 9.4), soft tissue
mass in the right hilar (SUVmax 10.8), several enlarged lymph nodes
right paratracheal, precarinal (both with SUVmax 9), right
supraclavicular fossa (SUVmax 5) and subcarinal area (SUVmax 4.7).
A 9mm lytic lesion is noted at S2 vertebral body with increase FDG
uptake, features suspicious of bony secondary.
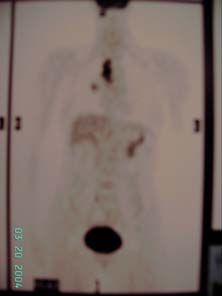

Figure 5 and 6, F18-FDG whole body PET scan
report : hyperdense mass with increased FDG
activitiy seen at the pineal area is suggestive of
primary or secondary brain tumor. In the chest, with
marked FDG uptake is compatible with primary
malignant lung tumor. Multiple lymph node
metastases including right paratracheal, precarinal
and right supraclavicular lymph nodes. Suspicious of
bony secondary to S2 vertebral body
figure 5
figure 6
No curative nor palliative surgery had been offered by the
cardiothoracic surgical team, as stage IV (distant metastases)
disease are considered inoperable.9. She subsequently undergone
WBRT (53.4Gy) and was followed up in out-patient clinic.
Discussion
Metastatic brain tumors occur more frequently than primary brain
tumors 10 but metastasis from lung carcinoma to pineal gland are
rare.2,11
18 FDG-PET offers a rapid method for whole-body imaging that
identifies systemic metastatic disease effectively and in assisting
those who are suitable for curative surgery, also used for
radiotherapy planning. 5 Negative PET scans can exclude metastatic
disease suggested by CT scans with a reported 1% false negative
rate. 2
However, because of the high metabolic rate of normal brain tissue,
PET is extremely poor at detecting cerebral metastases, with a
sensitivity of only 60%. 2 High - resolution MRI with gadolinium is
necessary in the evaluation of pineal region lesions. Tumor
characteristics (eg. size, vascularity, and homogeneity) and its
anatomic relationship with surrounding structures, can be assessed.
4
"Synchronous" brain metastasis had been defined as lesions
detected within 2 months of the primary diagnosis of related cancer
and those with an unknown primary or newly diagnosed brain tumor
with which the primary was unknown. This had been associated with
a poor prognosis with a survival of 9 14 months. 6
According to International System for Staging Lung Cancer 7 ,this
patient has (cT2, tumor status) with tumor size greater than 3cm in
the greatest dimension, N3 (nodal status) with evidence of
supra-clavicular lymph node metastasis and M1 (metastasis status)
with the presence of distant metastasis (S2 vertebrae). 5 year
survival in these patients with M1 were were expected to be around
1%.
The main treatment goals for patients with brain metastases in this
region include relief of neurological symptoms, as in our case, with
CSF diversion for relief of hydrocephalus, and long-term control of
the tumor.
Although there have been no prospective randomized studies
comparing stereotactic surgery (SRS) and external beam whole brain
radiation therapy (WBRT) to WBRT alone, there have been numerous
large retrospective series reporting a significant survival benefit from
SRS. Glucocorticoids and WBRT comprise the current standard of
care and increase median survival from one month to three to six
months. 10
However, the presence of VPS is believed to facilitate extraneural
metastasis of the intracranial metastasis. 13 Re-irradiation and
chemotherapy may have a limited role in patients with multiple
recurrent metastases. 12
References :
1) DeAngleis LM, Posner JB, Neurological complications of cancer , Chp 143
pp2251-70
2) Kent MS, Jeffrey LP et al , Current state of imaging for lung cancer
staging, Thoracic Surgical Clinic 14 (2004) 1 13
3) Jeffrey Bruce, Pineal Tumors, eMedicine Specialties, Neurosurgery,
Kakita A, Kobayashi K, Aoki N, Eguchi I, Morita T, Takahashi H.
Neuropathology. 2003 Mar; 23(1):57-60. Lung carcinoma metastasis
presenting as a pineal region tumor
4) Jeffrey Bruce, MD, Pineal Tumors, eMedicine Specialties >
Neurosurgery , section 1-11
5) Goldsmith SJ et al, Journal of Thoracic Surgical clinic 14 (2004) 95
112
6) Thomas AJ, Rock JP et al, Survival of patients with synchronous brain
metastases: an epidemiological study in southeastern Michigan,
Neurosurg Focus Preview: J Neurosurg 93:December 2000
7) CF Mountain, Revision in International System for Staging Lung Cancer,
Chest Vol 111, 1710-17, 1997
8) Kavitha Vadde, MD, Alan J. Fischman, MD PhD, Whole Body FDG PET
and Staging of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer, Joint Program in Nuclear
Medicine, January 18, 2000
9) G J M Herder et al , Practice, efficacy and cost of staging suspected
non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study in two Dutch hospitals,
Thorax 2002;57:11-14
10) Official Title: A Prospective, Randomized Trial Comparing Surgery
Versus Radiosurgery for the Treatment of Metastatic Brain Tumors,
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
11) Keyaki A et al, Pineal metastatic tumor from lung cancer initially
caused by neurological abnormalities of pineal body tumor Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 2000 Dec;1(5):447-58
12) Wen PY, Loeffler, Brain metastases. JS.Rev Neurol
(Paris).1992;148(6-7):477-87
13) Poon TK et al, Extraneural metastasis of pineal germinoma via VP
shunt, Ann Coll Surg HK (2004) 8, 153-5
Home • Journals • Search • Rules for Authors • Submit a Paper • Sponsor us
All pages copyright ŠPriory Lodge Education Ltd 1994-

